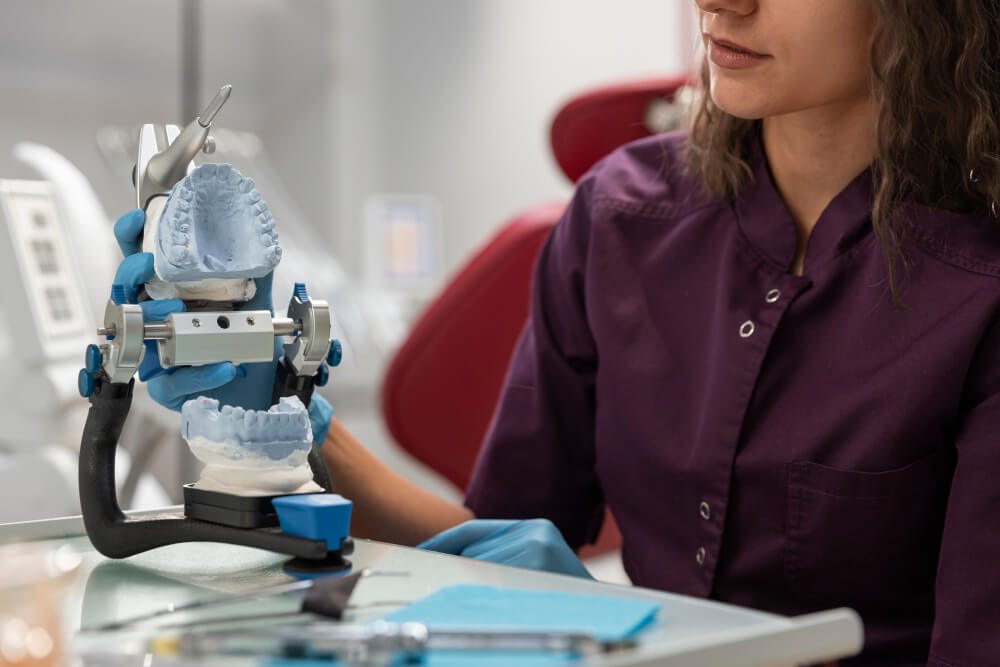
It has been well-documented that there exists an interdependence of neuromuscular function on oral health outcomes. Persons who have cerebral palsy, ataxia, or drug-induced xerostomia develop much higher rates of periodontal disease and caries than the general population (Journal of Disability and Oral Health, 2023). Assisteeze represents a new category of assistive technology that takes engineering principles and applies them to dentistry, developing validated neuro-motor oral care products. Its programmable micromotors, fluid micropumps, and pH detection sensors are not consumer gimmickry but products of rigorous dental biomechanics research. This integration of mechanical engineering and clinical dentistry puts Assisteeze on the cutting edge of preventive health care, where oral disease is detected and intercepted before it can develop.
Clinical Epidemiology and Unmet Needs
Epidemiological research discovers patients with neurological or physical impairment are 1.8–2.4× as likely to present untreated dental caries and gingivitis compared to control subjects (Canadian Dental Association, 2022). The gap is due to insufficient equipment, not patient non-compliance. Assisteeze bridges the gap through evidence-based neuro-motor oral care, enabling uniform brushing patterns across manual dexterity. Its scientifically based dental biomechanics research foundation guarantees that bristle forces are within safe ranges, minimizing enamel wear and maximizing plaque removal. The instrument is therefore simultaneously a rehabilitation instrument and a preventive clinical therapy, justified by population-level effects.
Engineering Validation Through Biomechanical Parameters
Forces of brushing greater than 0.4 N are also responsible for cervical abrasion and gingival recession (Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 2020). Too little force generates a failure in plaque removal. Assisteeze uses micro-gearbox control and torque sensing to deliver optimal ranges from research into dental biomechanics. Its application to neuro-motor oral care is mechanizing human brushing motions with repeatable accuracy, suppressing variability due to tremor or spasticity. Experimental studies have shown that metric uniform motor-driven tooth movement has greater plaque reduction scores than manual toothbrushing, which serves to justify its role as a research-validated intervention as compared to an assistive device.
Adaptive Algorithms for Personalized Oral Health
Preventive medicine is becoming more focused on individualization, as well as patient-specific physiological profiles (Government of Canada Health Innovations, 2023). Assisteeze achieves this in the form of adaptive algorithms that adjust brush speed, rotation angle, and suction cycles based on real-time sensor feedback. These attributes are optimized specifically for neuro-motor oral hygiene, embracing variability in motor coordination. Leveraging dental biomechanics research, the system adjusts brushing parameters to patient-specific dental morphology and occlusal forces. By combining personalization and biomechanics, Assisteeze redefines the paradigm of precision dentistry, precluding disease exacerbation through continuous harmonization of device performance with patient-specific demands.
Public Health and Canadian Systemic Integration
Canada’s oral health system is facing mounting pressure from an aging population and increased levels of chronic disease, with oral diseases being the most prevalent avoidable conditions (Euromonitor, 2021). Products such as Assisteeze have a crucial role to play in bridge-building across equity divides through evidenced-based neuro-motor oral care therapies. Building on dental biomechanics research, the product provides a scalable model for prevention that will meet Canada’s public health objectives for accessibility and equity. In minimizing caries incidence as well as the advancement of gingival disease among high-risk populations, Assisteeze reduces long-term national healthcare costs. It then becomes not only a consumer product but an instrument within the public health system.
Trust Through Clinical Evidence and Replicability
Clinical uptake is based on trial substantiated and reproducibility between trials. Initial clinical testing of Assisteeze under dental auspices shows statistically significant reductions in plaque and gingival index scores over regular brushing. These results place it in the class of evidence-based neuro-motor oral care solutions. The fact that it meets standards in research in dental biomechanics research, such as force control, pH stability, and ergonomic accommodation, contributes to clinical confidence. By presenting measurable outcomes as opposed to marketing hearsay, Assisteeze positions itself as an evidence-based, replicable intervention waiting to be integrated into streams of rehabilitation and preventive dental care.
Conclusion
The synergy of dentistry, neurology, and engineering is where the future of oral health lies. Assisteeze is such a synergy because it integrates micromotor design, torque control, and biochemical detection into a single science-supported platform. It is an example of neuro-motor oral care that seeks to fill gaps in low-dexterity populations. Its roots in dental biomechanics research separate it from consumer devices and position it in preventive, evidence-based practice. In the Canadian context, where innovation policy is guided by equity and inclusion, Assisteeze illustrates how science can systematically make oral health care an everyday practice a clinically sound solution.